ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) is a specialized remote-access client component of IBM Rational ClearCase, a widely used version control system designed to manage large-scale enterprise software development. While traditional ClearCase setups operate within a centralized network environment, the ClearCase Remote Client enables developers to work from virtually any location by connecting to a central ClearCase server over the internet.
This capability is especially critical in today’s distributed software development environments, where development teams often span continents and time zones. CCRC empowers these distributed teams to efficiently manage source code, track changes, and maintain consistency across collaborative projects without requiring full installations of ClearCase on local machines.
Definition of ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC)
ClearCase Remote Client, often abbreviated as CCRC, is a lightweight version of IBM Rational ClearCase that provides remote access to ClearCase repositories. It integrates seamlessly into Eclipse-based IDEs and supports Unified Change Management (UCM), offering developers access to version-controlled files, activities, baselines, and change sets, directly from their remote environments.
Here’s a quick definition table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Tool Name | ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) |
| Developer | IBM |
| Purpose | Provide remote access to ClearCase repositories |
| Integration | Eclipse IDE, UCM, SCM tools |
| Target Users | Distributed software development teams |
CCRC vs IBM Rational ClearCase – Key Differences
While both tools belong to the same family, they serve different use cases. Here’s how they differ:
| Feature | IBM Rational ClearCase (Full Client) | ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Full-featured local installation | Lightweight remote-access client |
| Use Case | On-premise, LAN-based teams | Remote and distributed teams |
| Performance | Fast on LAN | May require caching for optimal speed |
| IDE Integration | Optional | Strong Eclipse IDE integration |
| Disk Usage | High | Low |
Key takeaway: CCRC is not a replacement for ClearCase but rather a complementary tool that extends its usability into remote and cloud-based workflows.
Benefits of Using a Remote-Only ClearCase Client
The shift to distributed software teams has made tools like CCRC essential. Here are some of the biggest benefits:
- Mobility and Flexibility: Developers can work from anywhere with internet access, improving team collaboration.
- No Local Repository Replication Needed: Saves bandwidth and disk space by working directly with central repositories.
- Integrated Workflow: Compatible with IBM UCM and Eclipse, simplifying change tracking and review processes.
- Secure Connection to Central Repository: Works over secured protocols like HTTPS or VPN, protecting intellectual property.
- Minimal Setup for Developers: Reduces IT overhead since CCRC doesn’t require full client setup.
“In the age of hybrid and remote-first workforces, tools like ClearCase Remote Client provide the flexibility and structure teams need to maintain high-quality software development cycles.”
— IBM Rational Software Development Team
When Is CCRC Most Useful?
- Cross-site collaboration: For global teams working on a single product.
- Remote debugging: Developers can analyze and debug without being on-site.
- Contracted or freelance development: Provides secure, limited access to project repositories.
- Field operations and testing teams: Lightweight, remote-friendly access ideal for QA teams.
Why Use ClearCase Remote Client?
The ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) is more than just a lightweight interface to a version control system—it’s a strategic tool for scalable, secure, and efficient software development across globally distributed teams. In this section, we’ll explore the key reasons organizations opt for CCRC and how it fits into modern development workflows.
1. Empowering Distributed and Remote Teams
With the global shift to remote and hybrid work environments, teams need tools that allow them to work from anywhere without compromising on performance or security. CCRC was built with this need in mind. It allows remote developers to access, modify, and commit code from outside the local ClearCase network, helping maintain continuous integration and delivery pipelines.
Benefits for distributed teams:
- Consistent access to centralized code repositories.
- Synchronized development workflows, even across time zones.
- No need for full ClearCase installation, reducing onboarding friction for new or external team members.
According to IBM’s ClearCase documentation, “CCRC improves productivity for distributed teams by enabling remote access to critical configuration management data.”
2. Optimized for Low Bandwidth Environments
Unlike traditional version control tools that demand high-speed LAN connections, CCRC was specifically designed to work efficiently over wide-area networks (WANs). This means developers with slower or unstable internet connections can still:
- Browse large repositories
- Checkout and check-in files
- Work on UCM activities
- Retrieve baselines and perform merges
Caching mechanisms reduce the impact of network latency by storing frequently accessed files locally.
3. Secure and Centralized Access
CCRC maintains the centralized architecture of ClearCase, ensuring all data remains within the main repository. This provides advantages such as:
- Single source of truth: Developers always work with the latest codebase version.
- Auditability and compliance: All changes can be tracked and reviewed.
- Enhanced security: No local repository copies reduce the risk of intellectual property loss.
You can secure access with VPNs, SSL, and LDAP, aligning with enterprise-grade IT policies and compliance requirements.
4. Integration With IBM Rational Suite and IDEs
CCRC seamlessly integrates with Eclipse-based IDEs and other tools in the IBM Rational Software suite, including:
- Rational Team Concert (RTC)
- Rational Quality Manager (RQM)
- Rational Application Developer (RAD)
This allows developers to manage code, tasks, and test plans all in one place, reducing tool-switching and increasing productivity.
5. Unified Change Management (UCM) Support
One of the key features of CCRC is its support for Unified Change Management (UCM). UCM is a process framework that enforces structured workflows for:
- Activity-based development
- Stream and baseline management
- Code merging and conflict resolution
CCRC enables remote users to fully participate in UCM workflows, including:
- Creating and joining activities
- Delivering code to integration streams
- Creating baselines for testing and releases
Use Case Example
A financial software company with development teams in New York, Berlin, and Bangalore implemented CCRC to streamline their UCM-based workflows. The result: a 30% reduction in integration conflicts and a 25% increase in release frequency over 6 months.
6. Licensing and Cost Optimization
Deploying the full ClearCase client across hundreds of remote devices can be expensive and technically burdensome. CCRC provides a cost-effective alternative by reducing:
- Licensing overhead (only lightweight client licenses needed)
- IT support costs
- Machine resource usage
Organizations can scale access for contractors or remote employees without provisioning full installations.
Summary Table: Why Use ClearCase Remote Client?
| Reason | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Remote Access | Work from anywhere with internet |
| Lightweight Client | Easier installation and lower resource usage |
| WAN Optimization | Functions well over low-speed connections |
| Secure Centralized Control | Ensures compliance and data safety |
| Eclipse/IDE Integration | Streamlines developer workflows |
| UCM Compatibility | Supports structured and scalable development |
| Cost-Effective | Lower licensing and support costs |
How Does ClearCase Remote Client Work?
Understanding how ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) operates can help developers, project managers, and system admins appreciate its robust architecture and integration capabilities. CCRC is not just a stripped-down ClearCase interface—it’s a fully functioning remote version control gateway designed for distributed teams and enterprise-level projects.
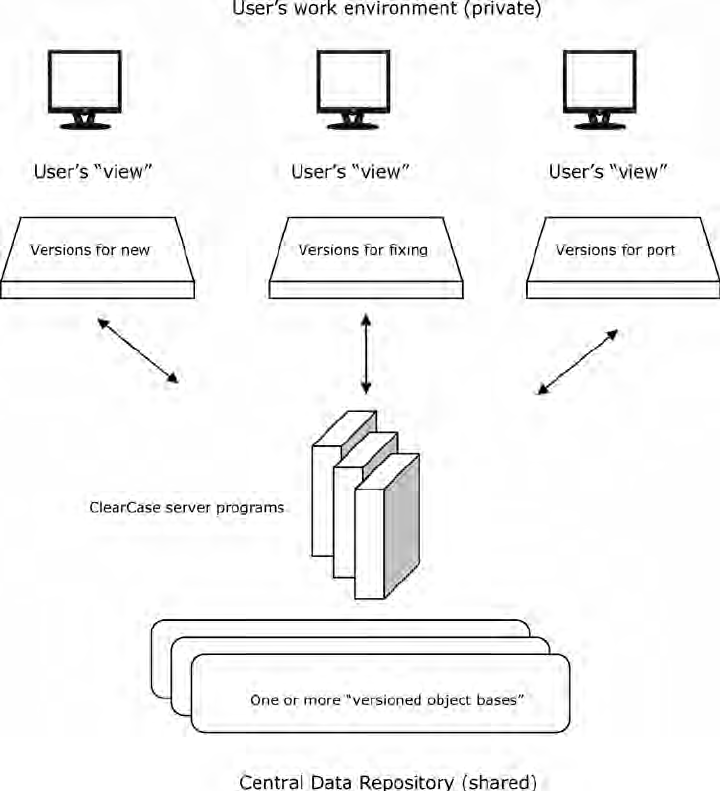
1. Architecture Overview of CCRC
At its core, CCRC uses a web-based communication layer to interact with IBM Rational ClearCase servers. Here’s how it works:
- Remote Client (CCRC): Installed on the developer’s machine, often as an Eclipse plugin.
- ClearCase Web Server (CM Server): Hosts the WebSphere Application Server or Tomcat-based service that communicates with the ClearCase repository.
- VOB and View Servers: These are the main components of traditional ClearCase where actual versioned objects and dynamic views are stored.
This three-tier setup allows developers to perform version control operations over HTTP/HTTPS, instead of relying on a LAN or VPN connection.
📘 For a detailed technical explanation, IBM’s ClearCase CCRC documentation is the most authoritative source.
2. Communication via Web Services
The ClearCase Remote Client communicates through SOAP-based web services using the HTTP or HTTPS protocol. This architecture ensures:
- Firewall-friendly access (no need to open exotic ports).
- Security through HTTPS encryption.
- Session persistence across slow or unstable connections.
This model is similar to how many cloud-native tools like GitHub or GitLab operate, but in a centralized on-premise environment.
3. Key Operations Supported by CCRC
Here are some critical operations that developers can perform using ClearCase Remote Client:
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| Check In/Out | Manage file versions in VOBs |
| Update Activities | Link changes to specific tasks |
| Merge Files | Resolve conflicts with baseline awareness |
| Browse Repository | Navigate source tree, views, and history |
| Create Baselines | Establish stable configurations for builds |
| Deliver and Rebase | Share work between streams |
These actions are done through an intuitive Eclipse-based GUI, helping developers avoid the steep learning curve that often accompanies complex version control systems.
4. CCRC and Web Views
One of CCRC’s core advantages is the use of Web Views, which are a lightweight alternative to local dynamic views or snapshot views. Here’s why Web Views matter:
- Files are not stored permanently on the local machine.
- They are fetched on-demand, reducing disk usage.
- Excellent for stateless workstations or virtual environments.
This is particularly useful for contractors or developers who frequently change workstations, or for large-scale development environments using Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI).
Read more about Web Views in this archived IBM Redbook on ClearCase: Implementing Rational ClearCase Remote Client
5. Integration with Eclipse IDE
CCRC was designed to integrate directly with Eclipse-based development environments, providing:
- In-editor version control actions (check-in, diff, annotate)
- Task-oriented navigation through UCM activities
- Stream-aware merging and rebasing
- Project-level visibility of code history
This integration reduces context switching and accelerates delivery pipelines by combining coding and configuration management into a single workspace.
For IDE integrations beyond Eclipse, consult IBM’s compatibility matrix: ClearCase System Requirements
6. Connectivity & Performance Optimization
CCRC uses multiple layers of optimization to ensure stable performance over WAN:
- HTTP caching of file metadata and diffs
- Compression of communication payloads
- Delta transfer for files instead of full copies
- Background syncing for check-ins/check-outs
These improvements mean even large teams can work efficiently without waiting on massive file downloads or redundant sync operations.
7. Security Protocols and Authentication
ClearCase Remote Client supports LDAP, Active Directory, and HTTPS authentication, making it ideal for enterprise setups. Security highlights include:
- Access control lists (ACLs) for VOBs and views
- Encrypted transmissions to protect IP over the internet
- Audit logs and user tracing for compliance purposes
IT teams can tightly integrate CCRC into their existing security infrastructure without compromising development speed.
Learn more from IBM’s official guidance on ClearCase Security Configuration.
Summary Chart: How CCRC Operates
| Layer | Description |
|---|---|
| Web Client | Developer-facing GUI via Eclipse |
| Web Application | SOAP/HTTP interface for remote actions |
| VOB Server | Central repository for versioned objects |
| View Server | Manages working views and checkouts |
| Security Layer | LDAP + HTTPS + Access Control |
Installing and Configuring ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC)
Installing and configuring ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) properly is crucial to ensuring a seamless and efficient development workflow. Whether you’re deploying CCRC for a single user or an entire enterprise team, the setup must align with your network, authentication, and repository infrastructure.
This section will guide you through:
- Prerequisites before installation
- Step-by-step installation guide
- Web server configuration
- Integration with Eclipse IDE
- Troubleshooting common issues
1. Prerequisites for Installing ClearCase Remote Client
Before installing CCRC, ensure your environment meets the following system and software requirements:
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows 10/11, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), SUSE Linux Enterprise |
| Java Version | JDK 8 or higher |
| Eclipse Version | Eclipse 4.6 (Neon) or later |
| Disk Space | Minimum 500MB free space |
| Web Server | IBM WebSphere Application Server or Apache Tomcat |
| Network Access | Port 80/443 access to CCRC Web Service (CM Server) |
| ClearCase Server Version | Must be compatible (e.g., CCRC 9.0.1 requires ClearCase Server 9.0.1) |
For the latest compatibility details, consult IBM’s official ClearCase system requirements guide.
2. Installing ClearCase Remote Client (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Download the Installer
Visit IBM Fix Central or IBM Passport Advantage to download the CCRC Eclipse plugin or standalone installer.
🔗 Download CCRC from IBM Fix Central
Step 2: Install the Eclipse Plugin or Standalone
You have two options:
- Eclipse Plugin: If using Eclipse IDE, install via
Help > Install New Software, then point to the local.zipor IBM update site. - Standalone Version: This version includes an embedded Eclipse environment preconfigured for ClearCase.
Step 3: Launch and Configure the Workspace
After launching, configure:
- Repository access (CM server URL)
- Authentication settings (LDAP, SSO, or local)
- Workspace directory for Web Views
Step 4: Validate Connectivity
Ensure CCRC can connect to the remote CM server using the test connection utility inside the preferences pane.
3. Configuring the Web Server (CM Server)
To allow remote clients to communicate, you must configure the ClearCase CM server, often running on IBM WebSphere or Tomcat. Here’s how:
- Install WebSphere Application Server (or Tomcat)
🔗 WebSphere Official Documentation - Deploy the CM Server WAR File
This file enables SOAP and HTTP/HTTPS communication between CCRC and ClearCase. - Configure SSL (HTTPS)
Use self-signed or enterprise CA-signed certificates for secure communication.
🔗 IBM TLS Security Guide - Set Up Authentication
Most enterprises use LDAP or Active Directory. Configure it within the application server. - Open Firewall Ports
Ensure ports 80 (HTTP) and 443 (HTTPS) are accessible to external clients.
Once complete, test the connection from a CCRC client to validate server accessibility.
4. Integration with Eclipse IDE
If you’re using CCRC as a plugin, you’ll get deep integration with your development environment. Benefits include:
- Source control operations integrated directly in the Project Explorer.
- Automatic change detection on file save.
- UCM activity tracking to associate changes with tasks or bugs.
- Compare/Merge tools built into the editor.
To activate ClearCase views:
- Open Eclipse.
- Go to
Window > Perspective > Open Perspective > Other > ClearCase Remote Client. - Configure your workspace and Web View.
If you’re using Rational Application Developer (RAD) or other IBM IDEs, CCRC support is native and seamless.
For more details, check IBM’s guide on Integrating CCRC with Eclipse
5. Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Here are some common issues users face when setting up CCRC—and how to resolve them:
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| “Unable to connect to CM server” | Check HTTPS port access and SSL certificates. |
| Plugin not visible in Eclipse | Ensure compatibility of Eclipse version and re-install plugin. |
| Web View fails to load | Clear workspace cache and verify server-side permissions. |
| Authentication failure | Validate LDAP credentials and test using basic HTTP client. |
| Slow performance | Use local caching options and check network latency. |
A detailed troubleshooting guide is available via IBM Support:
🔗 ClearCase Troubleshooting Docs
Best Practices for Setup
Here are some best practices to ensure optimal performance and security:
- Always install the latest Fix Packs from IBM.
- Use HTTPS with signed certificates to protect data in transit.
- Set up automated backup for views and VOBs.
- Document and version-control your CM server configurations.
- Provide user training to avoid misuse or accidental data loss.
Features and Capabilities of ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC)
The ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) is more than just a remote-access tool—it is a full-featured interface to IBM Rational ClearCase, enabling geographically distributed teams to collaborate efficiently and securely. CCRC combines the power of enterprise-grade version control with the flexibility of web-based and IDE-integrated access.
In this section, we’ll explore the core and advanced features of CCRC, including:
- Core version control operations
- Support for Unified Change Management (UCM)
- Web Views and Dynamic Views
- Offline development capabilities
- Integration with Eclipse and IBM Rational tools
1. Core Version Control Features
At its foundation, CCRC offers robust source control and change management features that support both centralized and distributed teams. These include:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Check-in / Check-out | Users can safely reserve files, edit them, and check in changes. |
| Branching & Merging | Supports parallel development and structured merges. |
| Version Tree View | Graphical display of version history and merges. |
| Labeling | Allows tagging of specific baselines or configurations. |
| History and Audit Trail | View logs of changes, authors, timestamps, and comments. |
These capabilities are accessible through both the GUI interface and Eclipse plugin, helping streamline workflows for both developers and configuration managers.
For further reading: IBM ClearCase Version Control Overview
2. Unified Change Management (UCM) Support
CCRC is fully compatible with ClearCase’s Unified Change Management (UCM) model, offering a high-level abstraction for managing complex software development projects. UCM enables:
- Activity-based development: Work is organized around specific tasks, bugs, or features.
- Baseline management: Automatically capture the configuration of an entire project at a specific point.
- Stream-based branching: Isolate work in development, integration, or release streams.
- Component reuse: Modularize systems into reusable components across projects.
This model is ideal for organizations needing process control, repeatability, and traceability in their development lifecycle.
🔗 Learn more about UCM in IBM ClearCase
3. Web Views and Dynamic Views in CCRC
ClearCase Remote Client uses Web Views, a lightweight substitute for traditional dynamic views. Web Views enable:
- Remote access over HTTP/HTTPS
- Simplified view storage management
- Access to ClearCase repositories without installing the full ClearCase client
Comparison between Web View and Traditional Dynamic View:
| Feature | Web View (CCRC) | Dynamic View (Full ClearCase) |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Lightweight, remote | Full installation required |
| Access Method | HTTP/HTTPS | MVFS (Multi-Version File System) |
| Caching | Local file cache | Files accessed on-demand |
| Offline Capability | Limited | Not available |
| Performance | Depends on network + cache | Fast on LAN |
Web Views are ideal for remote developers, consultants, or offshore teams, allowing them to contribute without needing a heavyweight infrastructure.
4. Offline Development Capability
One of CCRC’s most practical features is local caching, which enables limited offline work. When configured, files retrieved through Web Views are cached locally and can be modified even when the user is temporarily disconnected.
Benefits:
- Helps maintain productivity during outages or travel
- Local performance improvement
- Syncs with server when connection resumes
Limitations:
- Offline operations are limited to files previously accessed
- Merging and check-ins require re-connection
This feature makes CCRC a strong choice for globally distributed teams with intermittent connectivity.
5. IDE Integration and Developer Productivity
CCRC integrates directly into Eclipse-based IDEs, allowing developers to:
- Manage source control without leaving their code editor
- Use familiar version control UI (e.g., right-click > check-in)
- Automatically associate files with tasks or activities
- See version history, differences, and annotations inline
- Use the ClearCase perspective to navigate repositories
Supported IDEs include:
- Eclipse IDE for Java/Enterprise
- IBM Rational Application Developer
- IBM Rational Software Architect
- IBM Rational Team Concert (RTC)
This tight integration accelerates developer productivity and reduces the need to switch contexts, which can slow development.
🔗 IBM Guide: Integrating ClearCase with Eclipse
6. Benefits Summary
To recap, the major features and advantages of ClearCase Remote Client include:
- Access ClearCase repositories from anywhere
- Secure, encrypted communication (HTTPS)
- Lightweight web views with caching
- Full support for UCM and branching
- Seamless IDE integration
- Reduced infrastructure overhead for remote teams
CCRC is especially beneficial in modern DevOps and hybrid environments, where developers need the power of enterprise configuration management without the burden of installing full-fat tools.
ClearCase Remote Client Use Cases and Best Practices
The ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) is designed to support a wide variety of development environments, from small distributed teams to large enterprise-scale projects with strict compliance needs. In this section, we’ll explore real-world use cases, industry applications, and best practices to optimize your ClearCase Remote Client experience.
1. Common Use Cases of ClearCase Remote Client
ClearCase Remote Client supports a range of development models. Some of the most common use cases include:
a. Distributed Development Teams
Organizations with developers located across different geographic regions use CCRC to avoid latency and heavy infrastructure requirements. Instead of relying on MVFS or network shares, developers can use Web Views to access repositories remotely over HTTP/HTTPS.
Example: A multinational banking software company enables its offshore team in India to contribute code without installing full ClearCase locally by using CCRC.
b. Consultants and Temporary Developers
Consultants often work on short-term engagements and need quick access to a version-controlled environment. CCRC allows them to get started with minimal setup while preserving full auditability and process controls.
c. Secure Environments
For teams operating in regulated sectors such as aerospace, defense, or healthcare, CCRC provides a secure way to enforce access control, activity tracking, and compliance with industry standards like CMMI or ISO 26262.
d. Agile Teams Using Rational UCM
Teams practicing Agile methodologies often benefit from CCRC’s support for activity-based development and stream isolation. It allows multiple teams to work independently while maintaining alignment through UCM baselines.
2. Best Practices for ClearCase Remote Client
To get the most out of CCRC, follow these proven best practices:
a. Configure Web Views Thoughtfully
- Use Web Views for remote access and minimize view clutter.
- Assign meaningful view names to help developers identify context.
- Enable caching in large projects to improve performance.
b. Use Activity-Based Workflows
- Tie changes to tasks or activities for traceability.
- Encourage developers to create new activities for each feature or bug fix.
- Promote streams and baselines after quality assurance reviews.
c. Leverage UCM for Project Governance
- Use baselines to manage releases and integration points.
- Group related components together using UCM projects.
- Regularly rebase development streams to avoid merge conflicts.
d. Train Teams on IDE Integration
- Help developers integrate CCRC with their preferred IDEs like Eclipse or Rational Application Developer.
- Train them on right-click source control actions like check-out, check-in, and diff.
e. Establish Governance Policies
- Implement access control rules based on user roles.
- Set up auditing and change approval workflows.
- Enforce review gates before baseline promotions.
3. Case Study: Telecom Company Uses CCRC for Agile Rollouts
A large telecommunications company transitioned from legacy on-premises development to a hybrid cloud-based model. The team integrated IBM Rational ClearCase with Eclipse using the ClearCase Remote Client.
Challenges faced:
- Developers were located in 4 different time zones.
- Limited access to high-performance network infrastructure.
- Need for traceability and compliance with telecom standards.
Solution implemented:
- CCRC was deployed with Web Views and HTTPS access.
- Developers used Eclipse to manage changes directly from their IDEs.
- Streams and baselines were used to manage iterative Agile sprints.
Results:
- Development velocity increased by 25%.
- Cross-team collaboration improved.
- Compliance audits passed with zero issues due to traceable baselines.
4. Industry Applications of CCRC
ClearCase Remote Client is particularly useful in the following industries:
| Industry | Usage Scenario |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Compliance with strict version control and audit needs. |
| Telecom | Handling multiple concurrent streams for rapid releases. |
| Banking/Finance | Secure and auditable development for regulatory compliance. |
| Automotive | Managing software across ECU components with reuse and traceability. |
| Healthcare | Enforcing FDA compliance with source traceability and baseline locking. |
5. Comparison: CCRC vs. Full ClearCase vs. Modern Git-Based Tools
| Feature | CCRC | Full ClearCase Client | Git |
|---|---|---|---|
| Remote Access | Yes (Web Views) | No | Yes |
| Installation | Lightweight | Heavy (requires MVFS) | Lightweight |
| Branching | Stream-based (UCM) | Stream-based | Commit-based |
| Compliance Support | Excellent (Audit trail, UCM) | Excellent | Varies |
| Offline Work | Limited | No | Yes |
| IDE Integration | Eclipse, Rational tools | Rational tools | VS Code, IntelliJ, etc. |
🔗 External Resource: IBM ClearCase Product Page
🔗 Comparison Guide – Git vs. ClearCase: Perforce Article
Installing and Configuring ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC)
Setting up the ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) is a critical step to ensure a seamless integration into your development workflow. This section provides a step-by-step installation and configuration guide for both administrators and end users. Whether you’re setting up a new system or onboarding a developer, these instructions will help you get up and running efficiently.
1. System Requirements for ClearCase Remote Client
Before installing, verify that your system meets the following requirements:
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Windows 10/11, Linux (Red Hat, Ubuntu), macOS (limited support) |
| Java Runtime | Java SE 8 or later |
| Memory | Minimum 2 GB RAM (4 GB recommended) |
| Disk Space | 1 GB for installation + space for views |
| Network | Stable Internet/HTTPS connection to ClearCase server |
| IDE Compatibility | Eclipse-based IDEs (Eclipse, RAD, RSA, etc.) |
Tip: Check IBM’s official ClearCase System Requirements Guide for version-specific compatibility.
2. Downloading ClearCase Remote Client
You can download CCRC from the IBM Passport Advantage site if you are a licensed user, or access trial versions if evaluating the software.
- Visit IBM Passport Advantage
- Log in using your IBM ID
- Navigate to the software downloads section
- Search for “ClearCase Remote Client”
- Select the appropriate version and platform
- Download the installer
3. Installing ClearCase Remote Client
Once you’ve downloaded the installer:
On Windows
- Run the
setup.exefile as Administrator. - Choose the installation directory.
- Select ClearCase Remote Client (CCRC) option only.
- Accept the license agreement.
- Complete the installation process.
- Restart the computer if prompted.
On Linux
bashCopyEditchmod +x install.bin
./install.bin
Follow the GUI or terminal prompts to finish the installation.
Important: Make sure your firewall and proxy settings allow HTTP/HTTPS connections to the ClearCase Web Server.
4. Configuring ClearCase Remote Client
Once installed, you’ll need to configure the client:
a. Set Up Web Access
- Open CCRC.
- Click Window > Preferences > Team > ClearCase Remote Client.
- Enter the ClearCase Web Server URL (e.g.,
https://clearcase-server.company.com/ccrc). - Test the connection to verify access.
b. Create a Web View
Web views enable remote access to versioned elements.
Steps:
- Go to ClearCase Remote Views > New Web View.
- Provide a view name (e.g.,
dev_john_featureA). - Choose the UCM project or VOB to base the view on.
- Specify the activity or stream to track.
- Confirm and let the system initialize the view.
Note: Views are cached locally but operate over the network, so performance may vary with network speed.
c. Integrate with Eclipse
- Open Eclipse.
- Go to Help > Install New Software.
- Add ClearCase Remote Client plugin if not pre-installed.
- Configure it by linking the Web View.
5. Troubleshooting Installation Issues
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| CCRC cannot connect to server | Check proxy/firewall settings; verify URL and port |
| Plugin not showing in Eclipse | Ensure correct plugin version; restart Eclipse |
| Views fail to load | Clear cache; verify Web Server status |
| Performance is slow | Enable local caching; avoid large views |
Support Guide: IBM Rational ClearCase Troubleshooting Guide
6. Security Considerations
When deploying CCRC in enterprise environments, ensure:
- HTTPS is enforced for all communication.
- Use LDAP/Active Directory for authentication.
- Restrict view creation to authorized users.
- Regularly audit access logs for anomalies.
7. External Resources and Documentation
Here are some useful links to official documentation and third-party resources:
- 🔗 IBM ClearCase Documentation Hub
- 🔗 ClearCase Remote Client Setup Video (IBM)
- 🔗 Eclipse Integration Tutorial – IBM DeveloperWorks
- 🔗 Stack Overflow: CCRC Common Issues
With your ClearCase Remote Client now installed and configured, you’re ready to start managing source code in a secure, efficient, and distributed way. In the next section, we’ll explore how to work effectively with ClearCase Remote Client in daily development tasks, including check-ins, merges, rebases, and conflict resolution.
